Thyroid cancer occurs in the cells of your thyroid gland. According to Cancer.net, each year approximately 52,890 people will be diagnosed with thyroid cancer in the United States. In 2020, thyroid cancer will be most commonly diagnosed in people aged 15 to 29. It is the fifth most common cancer for women and the most common cancer for men aged 30 to 39.
The key to treating these cancers is detecting them early. When diagnosed and treated early, the five-year survival rate for thyroid cancer is 98%. If the cancer is located only in the thyroid, the five-year survival rate is almost 100%. However, each case is different, depending on the type and stage of the cancer.
Dr. Robert Constant, Board Certified Specialist in Internal Medicine, Endocrinology and Metabolism at the Diabetes and Endocrine Center of Orlando reports that “Thyroid cancer is becoming one of the more common cancers in modern times.†Today, new, more highly sensitive diagnostic testing can lead to faster detection of smaller cancers.
Different types of cancers can develop, affecting both the seriousness of the cancer and what type of treatment is required. There are several types of thyroid cancers:
- Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common, arising from the follicular cells that produce and store thyroid hormones.
- Follicular thyroid cancer also grows from the follicular cells in the thyroid and usually seen in people ages 50 and older.
- Anaplastic thyroid cancer is a rare follicular cell cancer that grows quickly and is more difficult to treat.
- Medullary thyroid cancer begins in the c-cell level of the thyroid gland. Certain genetic issues can cause this disorder.
- Other types of thyroid cancer can manifest more rarely in the human body.
The success in treating any cancer lies in the early diagnosis of the disease.
To help you understand thyroid cancer, we must first understand what the thyroid is and how it works.
What is the Thyroid and How Does it Work?
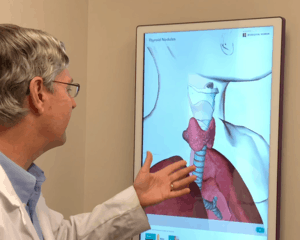 Your thyroid is a part of your endocrine system located at the base of your neck just below your Adam’s apple. A small butterfly-shaped organ that plays a big part in regulating your metabolism and the growth of the human body, it’s a complex tool consisting of small nodules enclosed within connective tissue. Each nodule contains hundreds of small follicles, or sacs, which store and secrete thyroid hormones.
Your thyroid is a part of your endocrine system located at the base of your neck just below your Adam’s apple. A small butterfly-shaped organ that plays a big part in regulating your metabolism and the growth of the human body, it’s a complex tool consisting of small nodules enclosed within connective tissue. Each nodule contains hundreds of small follicles, or sacs, which store and secrete thyroid hormones.
The thyroid produces hormones that regulate metabolism and growth. It affects all kinds of functions in the human body including digestive, heart, and muscle functions as well as bone maintenance and brain development. Most of the time this complex organ works in harmony with other bodily functions to regulate the level of hormones in your body. But there are several diseases of the thyroid, including cancer, that can affect your life and health.
What Could Go Wrong with the Thyroid Gland?
When the thyroid malfunctions it throws many bodily functions off. If the thyroid produces too much hormone, a condition called hyperthyroidism, weight loss, fast heart rate, irritability and nervousness, muscle weakness and tremors, and other symptoms can occur. In hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland produces too little hormone, causing weight gain, slower heart rate, fatigue, dry skin and hair, and more. Goiter is also often a symptom of hypothyroidism, causing enlargement of the thyroid gland.
Sometimes the thyroid can produce an abnormal growth of cells that form a lump within the thyroid gland. This is called nodular thyroid disease and it is very common and mostly benign. However, a small percentage of thyroid nodules can contain cancer cells.
What Are the Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer?
Early in the disease, thyroid cancer typically shows few symptoms. Typically, patients are diagnosed in three ways:
- When a patient notices a lump on their neck.
- A doctor detects swelling upon a routine exam.
- When patients undergo routine imaging tests such as an ultrasound or CT scan for some other type of health problem.
The symptoms of thyroid cancer could include:
- A lump or nodule that can be felt on the neck.
- Changes to your voice, including hoarseness.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Neck or throat pain.
- Swollen lymph nodes.
While there is no recommended clinical screening test for the detection of thyroid cancer, if your doctor suspects you have the disease, blood tests, a thyroid ultrasound, or a biopsy may be performed. A thyroid ultrasound uses a soundwave test for the anterior neck that gives the doctor a good image of the thyroid anatomy. A fine need aspiration (FNA) biopsy uses a very tiny needle to extract cells from the thyroid for analysis.
If cancer is found, other tests may be performed to find out more about the type of cancer. Your doctor will examine your complete medical history along with your family history to help determine the best course of treatment.
 What Treatments are Available for Thyroid Cancer?
What Treatments are Available for Thyroid Cancer?
Many cases of thyroid cancer can be detected early and treated successfully. The treatment options available depend upon a variety of factors, including the type of cancer, your overall health, and other factors that are individual to you, the patient. Your care team will discuss treatment options and it is important to weigh the risks, side effects, and possible health benefits of each type of treatment.
Depending upon the diagnosis, some of your treatment options may include:
- Surgery is a very common treatment for thyroid cancer. Removal of the tumor and all or part of the remaining thyroid gland may be recommended.
- After surgery, you will likely undergo thyroid hormone therapy to replace the missing hormones from the thyroid gland.
- Radioiodine therapy uses large doses of radioactive iodine to destroy the cancer cells.
- Â External radiation therapy aims high energy beams at precise points on your body to kill the cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy is a drug treatment that uses a variety of chemicals to kill the cancer cells.
- Targeted drug therapy hones in on specific elements of the cancer cells to disrupt their growth.
While these are typical treatments, new research yields treatments that improve our successes with thyroid cancers. For example, alcohol ablation is a newer procedure using ultrasound to guide an injection of concentrated alcohol solution into the neck to eliminate cancer cells. There are also palliative care options that seek to alleviate pain or other symptoms of serious illness. Your doctor may use one or several of these treatments to achieve the best outcome.
If you receive a cancer diagnosis, we understand how frightening it can be. But most thyroid cancers can be cured, especially if they are diagnosed early. Talk with our team. We offer the best treatment options, the most skilled team of clinical professionals, all in a comfortable setting designed to help you achieve wellness.




Leave A Comment